P^3-Based LearningFor purposes of this online toolkit, the P in PBL stands for project, phenomenon, or passion. During PBL, students use inquiry skills to investigate a problem, topic, or interest. Instead of discussing theories and reciting information, PBL lets learners achieve a meaningful product worth sharing with their community. Students apply the knowledge and skills gained during PBL to content from multiple subjects and situations. Learning extends well beyond the walls of the classroom.
|
Explore, Learn, Solve, Create With PBL, learners explore an engaging topic or respond to an authentic challenge. Students use a variety of sources to acquire new knowledge and make cross-curricular connections. Technology plays an important role, providing learners with information and creative possibilities. Through research and collaboration, students develop solutions and design products that fulfill learning goals. Using multimedia or another innovative approach, learners present their findings to an authentic audience.
|
Getting StartedCan you imagine trying to frame a house without a hammer or nails? What about trying to install a door without a drill or screws? These tasks require proper tools. The same is true for PBL. Students need specific tools to explore information and create new knowledge. This online toolkit provides the information and resources learners need to get started with PBL. Now is the time to use PBL to increase engagement, address learning standards, integrate technology, and prepare students for life outside the classroom.
|
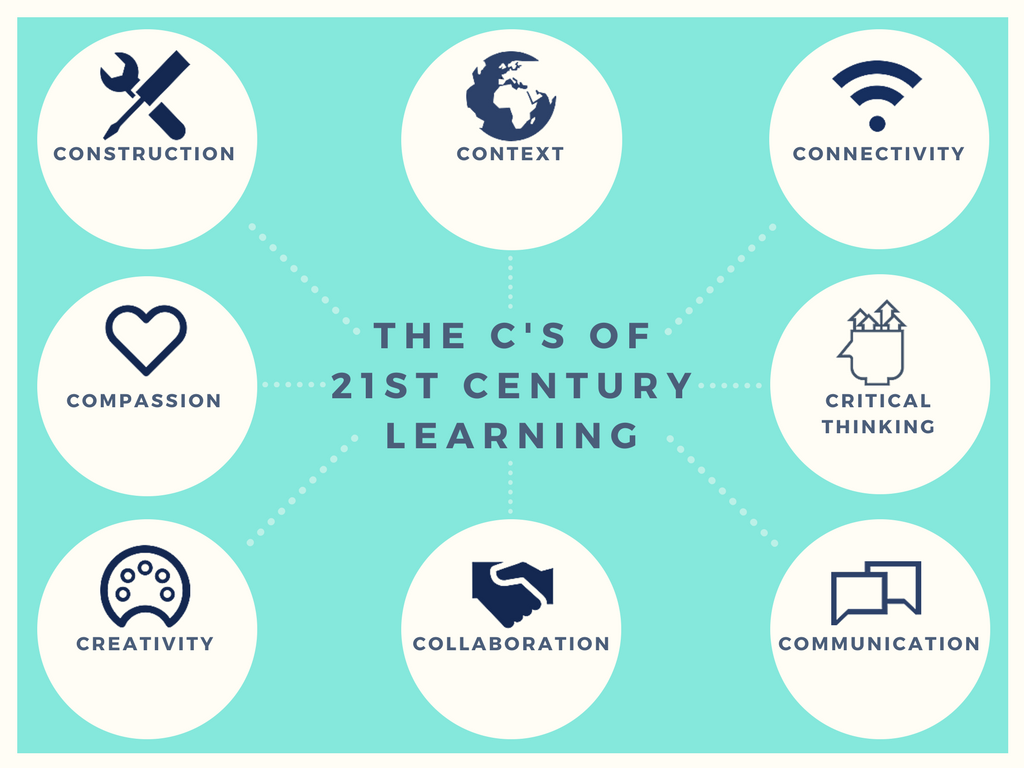
Accelerating 21st Century LearningIn a 21st century classroom, students take the driver’s seat. PBL gives students the green light to pursue their passions and explore the world. The road map spans many contexts, subject areas, and competences. Learners develop digital literacy skills as they navigate the information highway. Students no longer come to a screeching halt when they make a mistake. They learn from their failures and start again. Learners see detours as problems not yet solved. 21st century students do more than steer their learning toward a final goal. They question the current system and design new methods that improve the journey.
|
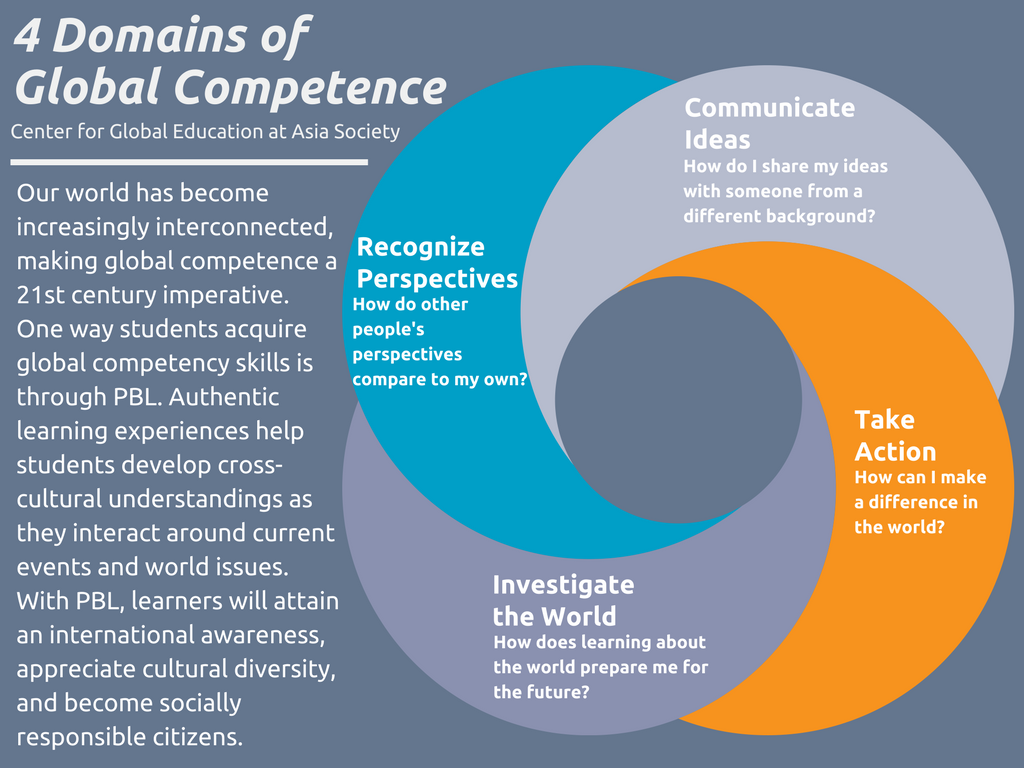
Promoting Global CompetenceGlobal competence is the capacity to examine local, global and intercultural issues, to understand and appreciate the perspectives and world views of others, to engage in open, appropriate and effective interactions with people from different cultures, and to act for collective well-being and sustainable development.
|